Methodology and Interpretation
Land cover diversity (Simpson index)
The diversity index is calculated by:
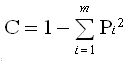 , Pi = the proportion of land cover type i. , Pi = the proportion of land cover type i.
Simpson's index is one of several ways to measure the diversity of land cover types within a
specific area of the landscape. Simpson's index is a measure of the evenness of the distribution
of land cover classes and is most sensitive to the presence of common land cover types within a
reporting unit. Simpson's index values range from 0 to 1, with 1 representing perfect evenness of
all land cover types within a reporting unit.
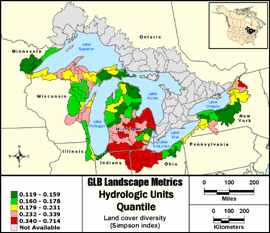
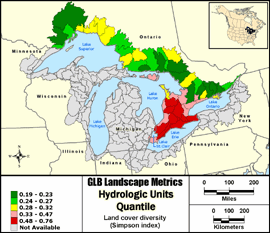
Quantile: Each class contains an approximately equal number (count) of features. A quantile
classification is well-suited to linearly distributed data. Because features are grouped by the number
within each class, the resulting map can be misleading, in that similar features can be separated into
adjacent classes, or features with widely different values can be lumped into the same class. This
distortion can be minimized by increasing the number of classes.
Metric input GIS data:
- United States Hydrologic Units (8-digit HUCs) - Metadata
- United States Coastal Change Analysis Program (CCAP) - Metadata
- Canada Hydrologic Units (Subsubdivisions) - Metadata
- Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources Data Set - Metadata
|