EPA On-line Tools for Site Assessment Calculation
| 43 of 67 |
Computing the Effective Diffusion Coefficient
The effective diffusion coefficient for layer i of a porous media can be estimated using the Millington relationship:
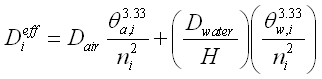
Contaminant Terms:
- Dair is the free-air diffusion coefficient for the contaminant of concern [cm2/sec].
- Dwater is the diffusivity in water for the contaminant of concern [cm2/sec].
- H is the dimensionless Henry's Law Constant for the contaminant of concern [unitless].
Soil Terms:
- ni is the total porosity of layer i of the porous media [unitless].
- θw,i is the water-filled porosity of layer i of the porous media [unitless].
- θa,i is the air-filled porosity of layer i of the porous media (θa = n - θw) [unitless].
The overall effective diffusion coefficient for systems composed of m layers (e.g., capillary fringe and the unsaturated zone) is:
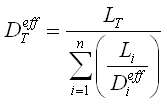
where Li is the thickness of layer i, LT is the distance between the source of contamination and the bottom of the slab (sum of all layer thicknesses) and Di eff is the effective diffusion coefficient for layer i.
The overall effective diffusion coefficient used in determining target soil-gas concentrations only considers diffusion through the single-layer unsaturated zone.
The overall effective diffusion coefficient used in determining target groundwater concentrations incorporates both diffusion through the capillary fringe and diffusion through the unsaturated zone.
|
Top ^
Home | Glossary | Notation | Links | References | Calculators |